What is n-type semiconductor?
What is n-type semiconductor Class 11?
The n-type semiconductor is created by adding pentavalent impurities in the semiconductor material, such as silicon and germanium. These pentavalent impurities can be phosphorus, antimony and arsenic, these impurities contribute free electrons, which greatly increases the conductivity of the intrinsic semiconductor.
Why is it called n-semiconductor? An impurity semiconductor that has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons.
What is semiconductor in physics class 11?
Semiconductors are those materials that exhibit conductivity between conductors (generally metals) and non-conductors or insulators (like ceramics). Semiconductors can be compounds like gallium arsenide or pure elements like germanium or silicon.
Why is it called semiconductor?
A semiconductor is called a semiconductor because it is a type of material that has an electrical resistance that is between the resistance typical of metals and the resistance typical of insulators, so it is a type of “semiconductor” for electricity.
What is semiconductor short notes?
Semiconductors, any of a class of crystalline solids with intermediate electrical conductivity between a conductor and an insulator. Semiconductors are used in the manufacture of various types of electronic devices, including diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits.
What are n-type and p-type semiconductors 12?
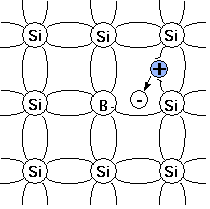
The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, a pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth, etc. The pentavalent impurities provide extra electrons and are called donor atoms.
What are n-type and p type semiconductors?
In an N-type semiconductor, most charge carriers are free electrons while holes are in the minority. In a P-type semiconductor, most of the charge carriers are holes, while the free electrons are in the minority.
What is n-type and P?
So what’s the difference? In n-type silicon, the electrons have a negative charge, hence the name n-type. In p-type silicon, the effect of a positive charge is created in the absence of an electron, hence the name p-type.
What is n-type and p-type semiconductors?
In an N-type semiconductor, most charge carriers are free electrons while holes are in the minority. In a P-type semiconductor, most of the charge carriers are holes, while the free electrons are in the minority.
What is n-type semiconductor explain?
What is an n-type semiconductor? An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Group IV silicon has four valence electrons and group V phosphorus has five valence electrons.
What is n-type and p-type semiconductors explain with examples?
P-N junction diodes consist of two adjacent pieces of p-type and n-type semiconductor materials. P-type and n-type materials are simply semiconductors such as silicon (Si) or germanium (Ge) with atomic impurities; the type of impurity present determines the type of semiconductor.
What is p-type and n-type in physics?
The fundamental difference between p-type and n-type semiconductors is that there is an excess of negatively charged charge carriers in an n-type semiconductor. In a p-type semiconductor there is an excess of positively charged charge carriers (holes, which can be viewed as the absence of an electron).
What are p- and n-type materials? P-type and n-type materials are simply semiconductors such as silicon (Si) or germanium (Ge) with atomic impurities; the type of impurity present determines the type of semiconductor.
What is p-type in physics?
What is P material? Semiconductors like germanium or silicon doped with one of the trivalent atoms like boron, indium or gallium are called p-type semiconductors. The foreign atom is surrounded by four silicon atoms. It provides the atoms to fill only three covalent bonds since it only has three valence electrons.
What is meant by p-type?
p-type in British English adjective. 1. (of a semiconductor) with a density of mobile holes greater than that of conduction electrons. 2. Associated with or resulting from the movement of holes in a semiconductor.
Why is p-type called p-type?
In n-type silicon, the electrons have a negative charge, hence the name n-type. In p-type silicon, the effect of a positive charge is created in the absence of an electron, hence the name p-type.
What is meant by P and N?
Item No. Per night. Item No. positive negative. Copyright 1988-2018 AcronymFinder.com, All Rights Reserved.
What is p in diode?
electronic symbol. A p-n diode is a type of semiconductor diode based on the p-n junction. The diode conducts current in only one direction and is made by connecting a p-type semiconducting layer to an n-type semiconducting layer.
What is N in pn junction?
In a semiconductor, the p-n junction is created by the doping process. The p-side or positive side of the semiconductor has excess holes and the n-side or negative side has excess electrons.
What is difference between p-type and n-type?
However, the main difference between the two is that a P-type semiconductor is obtained by adding the trivalent impurity like aluminum in a pure semiconductor, while an N-type semiconductor is obtained by adding a pentavalent impurity like phosphorus in a pure semiconductor .
What is meant by p-type and n-type semiconductor?
P-type semiconductors are positive-type semiconductors, which means a lack of 1 electron is required. N-type semiconductors are negative-type semiconductors, which means an excess of 1 electron is required. 4. In P-type semiconductors, majority carriers are holes and minority carriers are electrons.
What is n-type semiconductor explain?
What is an n-type semiconductor? An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Group IV silicon has four valence electrons and group V phosphorus has five valence electrons.
What do n-type and p-type semiconductors explain? The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, a pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth, etc. The pentavalent impurities provide extra electrons and are called donor atoms.
What is the function of n-type semiconductor?
An n-type semiconductor is formed by the implantation of dopant atoms, which have more electrons in their outer (bonding) shell than silicon. The resulting semiconductor crystal contains excess or free electrons available to conduct electricity.
What is n-type semiconductor used for?
An N-type semiconductor is a type of material used in electronics. It is made by adding an impurity to a pure semiconductor, such as silicon or germanium. The impurities used can be phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth or another chemical element.
What is n-type semiconductor and example?
Examples of n-type semiconductors are Sb, P, Bi and As. These materials contain five electrons in their outer shell. The four electrons will form covalent bonds using the neighboring atoms and the fifth electron will be accessible like a current carrier. This foreign atom is therefore referred to as a donor atom.
What is an n-type semiconductor Class 12?
N-Type Semiconductors: N-type semiconductors are formed by doping pure elements such as silicon (Si) and geranium (Ge) with 5 valence electrons with pentavalent impurities such as antimony (Sb), arsenic (As), or phosphorus (P). with four valence electrons.
What is n-type semiconductor and example?
Examples of N-type semiconductors are arsenic-doped silicon, phosphorus-doped silicon, germanium-doped arsenic, phosphorus-doped germanium, etc. are examples of n-type semiconductors.
What is the n-type and p-type semiconductor?
In an N-type semiconductor, most charge carriers are free electrons while holes are in the minority. In a P-type semiconductor, most of the charge carriers are holes, while the free electrons are in the minority.
Is p-type semiconductor positively charged?
Solution: No, a p-type semiconductor is not positively charged because it has a large number of holes and a small number of free electrons, since the total number of holes is equal to the total number of acceptor ions, which have opposite charges to each other, hence they cancel each other out since a p-type semiconductor…
Do p-type semiconductors have a net positive charge? The letter p in p-type semiconductors indicates the majority charge carriers and not the net charge in the semiconductor.
Why p-type semiconductor is positively charged?
Because an acceptor donates excess holes, which are considered positively charged, a semiconductor that has been doped with an acceptor is referred to as a p-type semiconductor; “p” stands for positive. Note that the material as a whole remains electrically neutral.
Is p-type semiconductor positively charged or negatively charged?
Therefore, a p-type semiconductor is electrically neutral, ie uncharged. So the correct answer is “Option C”. Note: Sometimes the p-type semiconductors are called acceptors because of the presence of the excess holes.
Why p-type semiconductor has negative ions?
The donor impurity in the n-type semiconductor loses an electron and becomes a positive ion. The p-type acceptor impurity accepts this electron and forms a negative ion. The “depletion region” immediately surrounding the junction is thus deficient in both electrons and holes.
Is p-type semiconductor negatively charged?
Therefore, a p-type semiconductor is electrically neutral, ie uncharged. So the correct answer is “Option C”.
Is p-type semiconductor charged?
The p-type semiconductor is uncharged or neutral since no charged particles are added in the semiconductors.
Is the p-type semiconductor negative?
…an n-type (negative) or p-type (positive) semiconductor. An n-type semiconductor is formed by the implantation of dopant atoms, which have more electrons in their outer (bonding) shell than silicon. The resulting semiconductor crystal contains excess or free electrons available to conduct electricity.
Are the n-type and p-type semiconductors positively and negatively charged?
P- and n-type materials are NOT positively and negatively charged. An n-type material itself has mostly negative charge carriers (electrons) that are free to move around, but it is still neutral because the solid donor atoms that donated electrons are positive. Was this answer helpful?
Is the p-type semiconductor negative?
…an n-type (negative) or p-type (positive) semiconductor. An n-type semiconductor is formed by the implantation of dopant atoms, which have more electrons in their outer (bonding) shell than silicon. The resulting semiconductor crystal contains excess or free electrons available to conduct electricity.
Is an n-type semiconductor negatively charged?
N-type semiconductors are neutral because neutral atoms are added during doping.


Comments are closed.