What is p-type semiconductor?
Where is the p-type semiconductor?
P-type semiconductors are made by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with an acceptor impurity. In p-type semiconductor, holes are majority carriers and electrons are minority carriers but are electrically neutral.
How are p-type materials formed? A p-type semiconductor is formed when a Trivalent impurity is added to a pure semiconductor.
How do you find the p-type semiconductor?
To make p-type semiconductors additional materials such as boron or aluminum are added to silicon. These materials have only three electrons in their outer shell. When the additive replaces some of the silicon it leaves a hole where the fourth electron would be if the semiconductor were pure silicon.
How do you identify a p-type semiconductor?
The easiest is to judge from the periodic table. If the dopant has more electrons in the outer shell than the semiconductor material, it will be n-type, and with fewer electrons in the outer shell, it is p-type.
How do we obtain n-type and p-type semiconductor?
P-type semiconductors are created when a group III element is doped onto a complete semiconductor material. In contrast, an n-type semiconductor is created when a group V element is doped onto an intrinsic semiconductor.
Why p-type semiconductor is called p-type?
Since the acceptor donates an excess of holes, which are assumed to be positively charged, the semiconductor that has been doped with the acceptor is called a p-type semiconductor; “p” means positive. Note that the material as a whole remains electrically neutral.
What is called p-type semiconductor?
What is P-type material? Semiconductors such as germanium or silicon doped with trivalent atoms such as boron, indium or gallium are called p-type semiconductors. The impurity atom is surrounded by four silicon atoms. This provides the atom to fill only three covalent bonds because it has only three valence electrons.
What is meant by p-type?
p-type in British English adjectives. 1. (of a semiconductor) having a moving hole density that exceeds the conduction electron density. 2. associated with or resulting from the movement of holes in a semiconductor.
What is the p-type of semiconductor?
What is P-Type Semiconductor? P-type semiconductors are intrinsic semiconductors doped with boron (B) or indium (In). Group IV silicon has four valence electrons and group III boron has three valence electrons.
What is p-type semiconductor Class 12?
Hint: A p-type semiconductor is formed when a pure semiconductor combines with an impurity. This results in holes in the combination. This is because three electrons from the impurity bond with four electrons from the valence shell leaving the fourth as a hole.
What is p-type semiconductor explain it with suitable example?
P-type :- When we use trivalent impurity for doping then we get p-type semiconductor. Examples of trivalent impurities are aluminum or boron. A semiconductor has 4 valance electrons in its outer orbit.
Is hole a positive charge?
In physics, holes are electric charge carriers with a positive charge, which is the same magnitude but opposite in polarity to the charge on the electron. Holes and electrons are two types of charge carriers which are responsible for the current in semiconductor materials.
How do holes act as positive charge carriers? Solution: Holes act as positive charge carriers When trivalent impurity is added to a tetravalent semiconductor then three electrons form covalent bonds with tetravalent silicon (SI) and hence the covalent bonds are left incomplete which are considered as holes.
Are holes negative charge carriers?
However, most circuits are designed based on conventional current, which uses positive charges moving in the opposite direction to the electrons. In addition to electrons and hypothetical positively charged particles, holes are also charge carriers.
Are holes in semiconductors positively charged?
Conclusion: Holes are quasiparticles of positive mass, positively charged.
Why do holes act as positive charge carriers?
Holes are considered positively charged because of the relationship between their speed and electric current: when they move to the right, the current goes to the right. It is theoretically possible to work only in the form of electrons: conduction band electrons and valence band electrons.
What is positive hole?
Positive holes in semiconductors are vacancies created at the location of a covalent bond when electrons leave a covalent bond.
Are electron holes positive?
Unlike electrons, which are negatively charged, holes have a positive charge of the same magnitude but opposite in polarity to the charge on the electron. Holes can sometimes be confusing because they are not physical particles like electrons, but rather the absence of electrons in atoms.
What is a positive hole?
If the hole associates itself with a neutral atom, that atom loses electrons and becomes positive. Therefore, the holes are considered to have a positive charge e, just the opposite of the electron’s charge.
What is the charge of a hole?
The hole charge is equal to the electron charge but has the opposite polarity. The charge on a hole is 1.6*10-19 coulombs. In semiconductor materials, holes & electrons are the ones that carry two types of charge. Hole mobility is less than electron mobility.
Do holes have charge?
A hole can be seen as the “opposite” of an electron. Unlike electrons, which are negatively charged, holes have a positive charge of the same magnitude but opposite in polarity to the charge on the electron.
Is hole a proton?
When we say “electron-deficient”, we really mean “the atom is initially neutral, then an electron is released, leaving an exposed proton that is not cancelled; a positive ion.” Holes are actually protons that are not canceled out of the silicon crystal lattice. They are really positively charged particles.
What type of semiconductor is silicon?
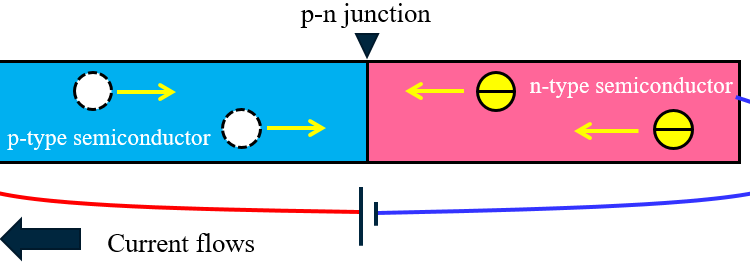
P-type semiconductors have more holes than electrons. This allows current to flow along the material from hole to hole but only in one direction. Semiconductors are most often made of silicon. Silicon is an element with four electrons in its outer shell.
Is it p-type or n-type silicon? N-type (Negative) A silicon atom has four electrons in its outer shell and is tightly bonded to the four surrounding silicon atoms creating a crystalline matrix with eight electrons in its outer shell.
Is n-type silicon a semiconductor?
What is an n-Type Semiconductor? An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), or antimony (Sb) as impurities. Group IV silicon has four valence electrons and Group V phosphorus has five valence electrons.
What is n-type and p-type in semiconductor?
The majority carriers in p-type semiconductors are holes. In n-type semiconductors, a pentavalent impurity of group V is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are Arsenic, Antimony, Bismuth etc. The pentavalent impurity donates an extra electron and is referred to as the donor atom.
Is silicon an n-type?
Silicon becomes an n-type semiconductor due to the addition of electrons. The arsenic atom is the donor. Similarly, Figure 2C shows that, when an atom with three outer electrons such as boron is replaced with a silicon atom, the additional electrons are ‘accepted’ to form four covalents.
What are types of semiconductor?
Semiconductors are divided into two categories: Intrinsic semiconductors. Extrinsic Semiconductor.
What are the types of semiconductor materials?
The most widely used semiconductor materials are silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide. Of the three, germanium is one of the earliest semiconductor materials used.
How many types of semiconductors do we have?
Found in thousands of electronic products, semiconductors are materials that conduct electricity more than insulators but less than pure conductors. There are four basic types of semiconductors.
Why is silicon p-type semiconductor?
What is P-type material? Semiconductors such as germanium or silicon doped with trivalent atoms such as boron, indium or gallium are called p-type semiconductors. The impurity atom is surrounded by four silicon atoms. This provides the atom to fill only three covalent bonds because it has only three valence electrons.
What makes up p-type semiconductor?
What is P-Type Semiconductor? P-type semiconductors are intrinsic semiconductors doped with boron (B) or indium (In). Group IV silicon has four valence electrons and group III boron has three valence electrons.
What are p-type silicon?
P-type (Positive) In contrast, p-type silicon is silicon doped with boron gas which turns it into a conductive material that readily accepts electrons when a voltage is applied. Boron has only three electrons in its outer shell and can only bond with three of the four silicon atoms around it.
What is p-type impurity?
P-type semiconductor is one type of semiconductor. When a trivalent impurity (such as Boron, Aluminum etc.) is added to an intrinsic or pure semiconductor (silicon or germanium), it is said to be a p-type semiconductor. Trivalent impurities such as boron (B), gallium (Ga), indium (In), aluminum (Al), etc.
How are p-type materials formed? P-type semiconductors are made by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with an electron acceptor element during manufacture. The term p-type refers to the positive charge of a hole. In contrast to the n-type semiconductor, the p-type semiconductor has a higher concentration of holes than the concentration of electrons.
What is p-type semiconductor materials?
What is P-Type Semiconductor? P-type semiconductors are intrinsic semiconductors doped with boron (B) or indium (In). Group IV silicon has four valence electrons and group III boron has three valence electrons.
What are p-type semiconductors used for?
P-type semiconductors have more holes than electrons. This allows current to flow along the material from hole to hole but only in one direction.
How is P-type material formed?
An extrinsic p-type semiconductor is formed when a trivalent impurity is added to a pure semiconductor in small amounts, and as a result, a large number of holes are created in it.
What are p-type substances?
A p-type semiconductor is an extrinsic type semiconductor. When a trivalent impurity (such as Boron, Aluminum etc.) is added to an intrinsic or pure semiconductor (silicon or germanium), it is said to be a p-type semiconductor. Trivalent impurities such as boron (B), gallium (Ga), indium (In), aluminum (Al), etc.
How is p-type material made?
An extrinsic p-type semiconductor is formed when a trivalent impurity is added to a pure semiconductor in small amounts, and as a result, a large number of holes are created in it. A large number of holes are provided in the semiconductor material by the addition of trivalent impurities such as Gallium and Indium.
What are types of p?
Related characters
- 𐤐 : The Semitic letter Pe, from which the following symbols come from. : the Greek letter Pi. …
- P with diacritics: á¹ á¹ á¹ á¹ â±£ áµ½ áµ± á¶
- Special symbols of the Ural Phonetic Alphabet associated with P: …
- p : The small p subscript was used in the Ural Phonetic Alphabet before its formal standardization in 1902.
What is p-type and n-type impurities?
The majority carriers in p-type semiconductors are holes. In n-type semiconductors, a pentavalent impurity of group V is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are Arsenic, Antimony, Bismuth etc. The pentavalent impurity donates an extra electron and is referred to as the donor atom.
What is the basic difference between p-type and n-type?
| N .-type semiconductor | P .-type semiconductor |
|---|---|
| Impurities in this material have the ability to take electrons, so they are called acceptor atoms. | In these materials, impurities provide electrons so these atoms are known as donor atoms. |
What is p and n-type impurities?
N-type semiconductor. P-type semiconductor. Impurities such as Arsenic, Antimony, Phosphorus and Bismuth (elements having five valence electrons) are added in N-type semiconductors. Impurities such as Aluminum, Gallium and Indium (elements having three valence electrons) are added in P-type semiconductors.


Comments are closed.