What is SiC structure?
Is SiC brittle?
Although brittle in nature, silicon carbide ceramics are leading materials for rotating and stationary components in many mechanical applications. They are characterized by low fracture toughness and limited strain-to-failure compared to metals.
Is silicon carbide durable? The physical durability of SiC is best demonstrated by looking at some of its applications outside of electronics: it is used in sandpaper, extrusion dies, bulletproof vest plates, high-performance brake discs, and flame arresters. SiC will leave scratches on an object rather than being scratched itself.
Which is harder SiC or diamond?
It is sometimes mistakenly compared to diamond, as diamond sits at 10 on the Mohs scale, one level above silicon carbide. However, the hardness of diamond is almost 3 times that of silicon carbide. However, SiC is still extremely hard.
Is anything harder than diamond?
The scientists found that Q-carbon is 60% harder than diamond-like carbon (a type of amorphous carbon with similar properties to diamond). This led them to expect Q-carbon to be harder than diamond itself, although this remains to be experimentally proven.
Is SiC harder than diamond?
For a naturally occurring mineral, silicon carbide – found naturally in the form of moissanite – is only slightly less hard than diamonds. (It’s still harder than some spider silk.)
What are the properties of SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC)
- Low density.
- High strength.
- Good high temperature strength (reaction coupled)
- Oxidation resistance (coupled reaction)
- Excellent resistance to thermal shock.
- High hardness and wear resistance.
- Excellent chemical resistance.
- Low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity.
What type of material is SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a hard covalently bonded material. A SiC compound consists of a silicon (Si) atom and four carbon (C) atoms that are covalently bonded between two of them. Silicon carbide (SiC) is a non-oxide ceramic engineering material that has gathered a considerable amount of interest.
What is the strength of silicon carbide?
| Property | Minimum Value (S.I.) | Units (Imp.) |
|---|---|---|
| Modulus of Breakage | 130 | ksi |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.35 | NULL |
| Shear Modulus | 32 | 106 psi |
| Tensile Strength | 240 | ksi |
Why is SiC transparent?
But why is SiC transparent? This is related to its wide band gaps. As you know, SiC is a compound of silicon and carbon, which form a semiconductor material with a wide band gap.
What kind of crystal is SiC? Silicon carbide (SiC) is a covalent network solid.
Is SiC soluble in water?
Insoluble in water. Soluble in molten alkalis (NaOH, KOH) and molten iron.
Does silicon carbide melt?
The melting of silicon carbide was studied at pressures 5–8 GPa and temperatures up to 3300 K. It was found that SiC melts coherently, and its melting curve has a negative slope of –44±4 K/GPa.
What is SiC in chemistry?
silicon carbide, an extremely hard, synthetically produced crystalline compound of silicon and carbon. Its chemical formula is SiC.
Is SiC transparent?
Pure SiC is colorless and very transparent in the visible; hexagonal SiC shapes are birefringent.
What type of material is SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a non-oxide ceramic engineering material that has gathered a considerable amount of interest. The SiC particles present relatively low thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, high hardness, and resistance to abrasion and corrosion.
What solid is SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a covalent network solid. If we look at its structure, we will find that the atoms of silicon are joined with carbon atoms by means of a tetrahedral covalent bond.
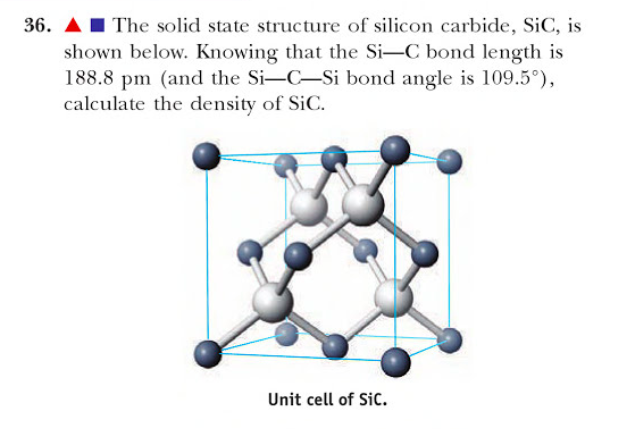
What is the structure of SiC?
How is SiC made?
Typically, Silicon carbide is produced using the Acheson process which involves heating silica sand and carbon to high temperatures in an Acheson graphite resistance furnace. It can be formed as a fine powder or a bound mass that must be crushed and ground before it can be used as a powder raw material.
What are the properties of SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC)
- Low density.
- High strength.
- Good high temperature strength (reaction coupled)
- Oxidation resistance (coupled reaction)
- Excellent resistance to thermal shock.
- High hardness and wear resistance.
- Excellent chemical resistance.
- Low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity.
What solid is SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a covalent network solid. If we look at its structure, we will find that the atoms of silicon are joined with carbon atoms by means of a tetrahedral covalent bond.
Is SiC covalent or molecular? SiC is a covalent network solid in which atoms of silicon are linked with carbon atoms tetrahedrally.
Is SiC is molecular solid?
SiC (Silicon Carbide)AINDiamond`I_(2)`. Solution : (a, b, c) are not molecular solids. These are covalent or network solids.
Is SiC a molecular carbide?
| SiC | Silicon Carbide |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight/Molar mass | 40.11 g/mol |
| Melting point | 2,730 °C |
| Compound Formula | SiC |
Is SiC simple molecular?
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (/ËkÉËrbÉËrÊndÉm/), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon.
What type of material is SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a non-oxide ceramic engineering material that has gathered a considerable amount of interest. The SiC particles present relatively low thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, high hardness, and resistance to abrasion and corrosion.
What is SiC metal?
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (/ËkÉËrbÉËrÊndÉm/), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal since 1893 for use as an abrasive.
Is SiC an abrasive?
Grinding requires rapid material removal and SiC is an obvious choice due to its abrasive properties when used on ferrous and non-ferrous metals, piping, construction, welding, casting and metallurgical markets.
What types of crystal is SiC?
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (/ËkÉËrbÉËrÊndÉm/), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal since 1893 for use as an abrasive.
Is SiC ionic or covalent?
Silicon carbide (carborundum) has the chemical formula SiC. Because this compound is bound by a strong covalent bond, it has a high m.p. (2700oC).
What is the structure of SiC?
How are SiC wafers made?
SiC balls (crystals) are grown, machined into ingots, and then cut into substrates, which are then polished. A thin SiC epitaxial layer is then grown on top of this substrate to create an epi-wafer.
How is a silicon carbide wafer made? This type of wafer is created by adding layers of single silicon carbide crystals to a surface. This method requires precise control of the thickness of the material, and is referred to as n-type epitaxy. The next type is beta silicon carbide. Beta SiC is produced at temperatures higher than 1700 degrees Celsius.
How are silicon carbide wafers used?
SiC is used for the manufacture of very high-voltage and high-power devices such as diodes, power transistors, and high-power microwave devices.
How are wafers used in semiconductors?
In electronics, a wafer (also called slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as crystalline silicon (c-Si), used for the manufacture of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to produce solar cells. The wafer serves as the substrate for microelectronic devices embedded in and on the wafer.
What is the purpose of a wafer?
A wafer is a piece of silicon (one of the most abundant semiconductors available worldwide) or other semiconductor material, designed in the form of a very thin disc. Wafers are used to create electronic integrated circuits (ICs) and silicon-based photovoltaic cells.
How much does a SiC wafer cost?
Today’s epi-ready 150 mm SiC wafers are sold for $750-$900, and 200 mm wafers are expected to be priced at $1300-$1800.
What is a SiC wafer?
SiC wafer is a semiconductor material that has excellent electrical and thermal properties. It is a high-performance semiconductor that is ideal for a wide variety of applications. In addition to its high thermal resistance, it also presents a very high level of hardness.
What is 4H SiC wafer?
4 = 4H-SiC. polytype Wafers are âoff-axisâ such that the wafer surface normal is oriented 4 degrees away from the [0001] plane, towards the [11-20] direction. 4 = 4° Off axis (n-type only) Wafers are âon-axisâ such that the wafer surface normal is parallel to the [0001] direction.
What is SiC wafer?
A silicon carbide wafer possesses superior physical and electronic properties compared to both silicon and gallium arsenide for certain short wavelength optoelectronic, high temperature, radiation immune and high power applications.
What are SiC semiconductors?
SiC (silicon carbide) is a compound semiconductor composed of silicon and carbide. SiC provides a number of advantages over silicon, including 10x the breakdown electric field strength, 3x the band gap, and enabling a wider range of p- and n-type control needed for device construction.
What does SiC mean in electronics?
AI or AIN = Analog Input.
Sources :


Comments are closed.