What is N-type material?
What are the 2 types of semiconductor?
Semiconductors are divided into two categories: Intrinsic semiconductors. Extrinsic semiconductor.
What is a semiconductor and its types? A semiconductor material is a substance that has an electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and a non-conductor or insulator. These are pure elements such as silicon, germanium, tin or compounds such as gallium arsenide (GaAs), copper oxide (Cu2O) and iron oxide (FeO).
What is semiconductor Name any two?
Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called “metalloid staircase” on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave frequency integrated circuits and others.
What is called semiconductor?
A semiconductor is a substance that has specific electrical properties that allow it to serve as the basis for computers and other electronic devices. It is usually a solid chemical element or compound that conducts electricity under certain conditions but not under others.
What is basic semiconductor?
Semiconductor materials such as silicon (Si), germanium (Ge) and gallium arsenide (GaAs) have electrical properties somewhere in the middle between ‘conductor’ and ‘insulator’ properties. They are not good conductors or good insulators (hence the name âsemiconductors).
How is n-type semiconductor formed Class 12?
N-type semiconductors are created by adding pentavalent impurities to a semiconductor material such as silicon and germanium. These pentavalent impurities can be phosphorus, antimony and arsenic, these impurities contribute free electrons, greatly increasing the conductivity of the intrinsic semiconductor.
What is N-type semiconductor explain? What is an n-type semiconductor? An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As) or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Group IV silicon has four valence electrons, and group V phosphorus has five valence electrons.
How is an N-type semiconductor formed name the major charge carriers in it?
1 Answer. When pentavalent impurity atoms Bi, Sd or P are doped in a pure germanium or silicon semiconductor, we get an n-type semiconductor. Electrons are the main charge carriers in it.
How is an n-type semiconductor is formed?
An n-type semiconductor is formed by implantation of dopant atoms that have more electrons in their outer (bonding) shell than silicon. The resulting semiconductor crystal contains excess or free electrons that are available to conduct current.
What are the main charge carriers in n-type semiconductor?
We add pentavalent impurities to the n-type semiconductor so that there is an excess of electrons inside the material. So, the main charge carriers are electrons.
How are n-type and p-type semiconductors formed?
n-type and p-type semiconductors are created by doping pure crystals such as silicon, germanium, etc., with pentavalent and trivalent elements. Explanation: Extrinsic semiconductors are a type of conductor produced by a process called doping.
How are p and n-type materials created?
A PN junction is formed when n- and p-type material are fused together to form a semiconductor diode. It all boils down to a p-n junction. N-type silicon has extra electrons, and on the p-side there are atoms that need electrons, so electrons migrate across the junction.
How is N-type semiconductor being created?
To make an n-type semiconductor, pentavalent impurities such as phosphorus or arsenic are added. Four impurity electrons form bonds with surrounding silicon atoms. This leaves one electron free. The resulting material has a large number of free electrons.
How is an N-type semiconductor formed?
An n-type semiconductor is created by introducing a pentavalent dopant. An example of a pentavalent impurity is phosphorus or arsenic. When trivalent impurities are used for doping, p-type semiconductors are formed. Aluminum and boron are examples of trivalent impurities.
What is p-type semiconductor 12?
(ii) p-type semiconductor: When a pure semiconductor is doped with a trivalent impurity (B, Al, In, Ga), then the three valence electrons of the impurity bond with three of the four valence electrons of the semiconductor. This creates an empty electron (hole) in the impurity atom.
What is a p-type semiconductor topper? A p-type semiconductor is formed when trivalent elements are used to dope pure semiconductors, such as Si and Ge. As can be seen in the figure above, when a trivalent atom takes the place of a Si atom, three of its electrons bond with three neighboring Si atoms.
What is p-type semiconductor?
What is a p-type semiconductor? A p-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with boron (B) or indium (In). Group IV silicon has four valence electrons, and group III boron has three valence electrons.
What is difference between n-type and p-type semiconductor?
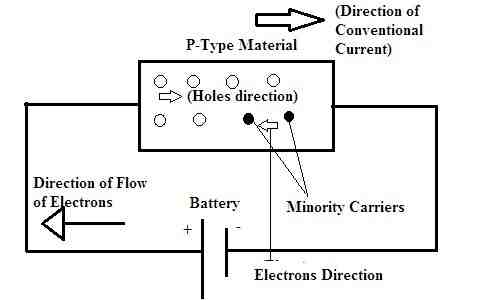
In an N-type semiconductor, electrons are the majority carriers and holes are the minority carriers. In a P-type semiconductor, holes are the majority carriers and electrons are the minority carriers. In these substances, most carriers range from high to low potential.
What are the p-type semiconductors called?
Semiconductors such as germanium or silicon doped with any of the trivalent atoms such as boron, indium or gallium are called p-type semiconductors.
What is n-type semiconductor Give Example 12?
N-Type Semiconductors: N-Type Semiconductors are formed by doping pure elements such as silicon (Si) and geranium (Ge) that have 5 valence electrons with pentavalent impurities such as antimony (Sb), arsenic (As) or phosphorus (P). which has four valence electrons.
What are semiconductors give examples Class 12?
Semiconductors can be compounds such as gallium arsenide or pure elements such as germanium or silicon. Physics explains the theories, properties, and mathematical approach that governs semiconductors. Examples of semiconductors: Gallium arsenide, germanium and silicon are some of the most commonly used semiconductors.
What is n-type and p type semiconductor example?
The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, a pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth, etc. Pentavalent impurities give extra electrons and are called donor atoms.
How are n-type and p-type semiconductor materials formed?
A p-type semiconductor is formed when group III elements are doped into a complete semiconductor material. Conversely, an n-type semiconductor is formed when group V elements are doped onto an intrinsic semiconductor.
Why is it called an n-type semiconductor? An extrinsic semiconductor that is doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because most of the charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons.
What is n-type semiconductor example?
Examples of n-type semiconductors are Sb, P, Bi and As. These materials include five electrons in their outer shell. Four electrons will form covalent bonds with neighboring atoms, and the fifth electron will be available as a current carrier. So the impurity atom is called a donor atom.
What are the examples of n-type?
Examples of N-type semiconductors Examples of N-type semiconductors are arsenic-doped silicon, phosphorus-doped silicon, germanium-doped arsenic, phosphorus-doped germanium, and so on are examples of n-type semiconductors.
What is n-type and p-type semiconductor example?
The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, a pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth, etc. Pentavalent impurities give extra electrons and are called donor atoms.
What is n-type semiconductor?
An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As) or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Group IV silicon has four valence electrons, and group V phosphorus has five valence electrons.
What is an n-type semiconductor Class 12?
N-Type Semiconductors: N-Type Semiconductors are formed by doping pure elements such as silicon (Si) and geranium (Ge) that have 5 valence electrons with pentavalent impurities such as antimony (Sb), arsenic (As) or phosphorus (P). which has four valence electrons.
What is N and p-type semiconductor?
The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, a pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth, etc. Pentavalent impurities give extra electrons and are called donor atoms.
What is N and P semiconductor?
The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, a pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth, etc. Pentavalent impurities give extra electrons and are called donor atoms.
What is the use of p and n-type of semiconductor?
Applications of n-type and p-type semiconductors npn and pnp transistors are used to detect or amplify radio or audio signals. A solar cell is an efficient photo-diode that is used to convert light energy into electrical energy.
What mean p and N types of conductivity of semiconductor?
This means that for n-type semiconductors, ionized donor atoms, positive ions, can cause electrostatic attraction with donated electrons, while in p-type semiconductors, ionized acceptor atoms (negative ions) cause electrostatic attraction with holes created in the lattice.
Sources :


Comments are closed.