Understanding Busbars: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of electrical engineering, the term “busbars” frequently appears as a vital component in power distribution systems. Busbars are essential for distributing electric power efficiently and safely, serving as a backbone for complex electrical networks. This article delves into the intricacies of busbars, exploring their types, applications, advantages, and installation considerations.
What Are Busbars?
Busbars are metallic strips or bars, typically made of copper, aluminum, or brass, that conduct electricity within a switchboard, distribution board, substation, or other electrical apparatus. Their primary function is to carry significant currents and distribute power across various circuits.
Types of Busbars
Understanding the different types of busbars is crucial for selecting the right one for your application. Here, we explore the various types:
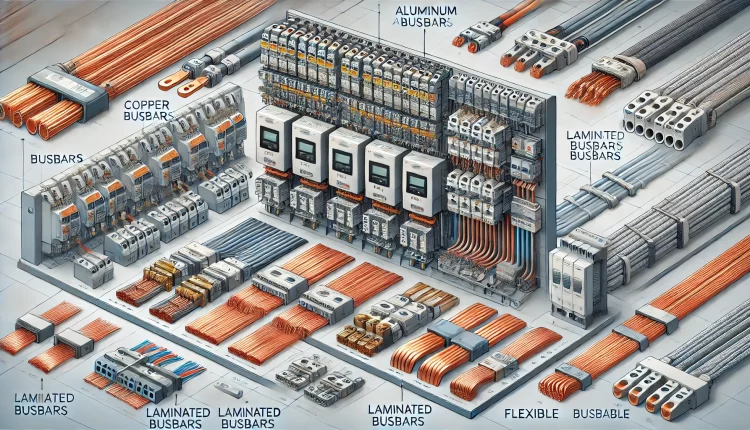
Copper Busbars
Copper busbars are renowned for their excellent conductivity and thermal properties. They are often used in applications where high electrical conductivity and durability are required. Copper busbars can handle high current loads and are resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Aluminum Busbars
Aluminum busbars are a cost-effective alternative to copper. They are lighter in weight and easier to handle, making installation more straightforward. Despite having lower conductivity than copper, aluminum busbars are widely used in industrial applications due to their affordability and adequate performance in many scenarios.
Laminated Busbars
Laminated busbars consist of multiple layers of conductive material separated by thin insulating materials. This design reduces inductance and improves performance by minimizing voltage drop and electrical noise. Laminated busbars are commonly used in high-frequency applications and environments where space is limited.
Flexible Busbars
Flexible busbars, also known as flexible bus connectors, are made from thin layers of copper or aluminum that are woven or laminated. They provide flexibility, allowing for easy installation in confined spaces and accommodating thermal expansion and contraction. Flexible busbars are particularly useful in applications where movement or vibration is expected.
Applications of Busbars
Busbars play a pivotal role in various industries, thanks to their versatility and efficiency. Below are some typical applications:
Power Distribution Systems
In power distribution systems, busbars are used to distribute electricity from a single source to multiple circuits. They ensure that power is distributed evenly and reliably, reducing the risk of overloads and enhancing system efficiency.
Electrical Panels and Switchgear
Busbars are integral components of electrical panels and switchgear, where they provide a central point for connecting incoming and outgoing circuits. They simplify the design and layout of electrical systems, making them easier to manage and maintain.
Renewable Energy Systems
In renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power installations, busbars are used to connect multiple photovoltaic (PV) modules or wind turbines to the power grid. They help manage the high currents generated by these systems and ensure efficient power distribution.
Data Centers
Data centers require robust and reliable power distribution systems to ensure the continuous operation of servers and other critical equipment. Busbars are used to distribute power within data centers, offering flexibility, scalability, and ease of maintenance.
Advantages of Using Busbars
Busbars offer several advantages over traditional wiring methods, making them a preferred choice in many applications:
Enhanced Efficiency
Busbars provide a low-impedance path for electrical current, reducing energy losses and improving system efficiency. This results in lower operational costs and better performance.
Space Saving
Busbars require less space compared to conventional wiring, allowing for more compact and streamlined electrical installations. This is particularly beneficial in environments with limited space, such as data centers and industrial control panels.
Improved Reliability
Busbars offer high mechanical strength and are less prone to damage compared to cables. They also provide a secure and stable connection, reducing the risk of loose connections and electrical faults.
Simplified Maintenance
The modular design of busbars makes it easier to add or remove components without disrupting the entire system. This simplifies maintenance and allows for quick and efficient upgrades or repairs.
Installation Considerations
Proper installation of busbars is crucial to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Here are some key considerations:
Material Selection
Choosing the right material for your busbars is essential based on your specific application requirements. Copper and aluminum are the most common materials, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Sizing and Rating
Busbars must be sized and rated correctly to handle the expected current load without overheating. Proper sizing ensures efficient power distribution and reduces the risk of electrical faults.
Insulation and Protection
Busbars should be adequately insulated and protected to prevent accidental contact and short circuits. This is especially important in high-voltage applications where safety is paramount.
Thermal Management
Busbars can generate significant heat during operation, so proper thermal management is essential. This can include using heat sinks, ventilation, or forced cooling systems to dissipate heat and maintain safe operating temperatures.
Busbars in Modern Electrical Systems
The role of busbars in modern electrical systems cannot be overstated. They are a key component in ensuring the efficient and reliable distribution of power across various applications. As technology advances and power demands increase, busbars continue to evolve to meet the challenges of contemporary electrical systems.
Emerging Trends in Busbar Technology
The field of busbar technology is constantly evolving, with innovations aimed at improving performance and efficiency. Here are some emerging trends:
High-Density Busbars
High-density busbars are designed to handle higher current loads in compact spaces. They are beneficial in applications where space is at a premium, such as data centers and industrial control panels.
Smart Busbars
Smart busbars integrate sensors and monitoring systems to provide real-time data on electrical performance. This allows for proactive maintenance and helps prevent potential issues before they become critical.
Eco-Friendly Materials
With a growing focus on sustainability, there is an increasing demand for busbars made from eco-friendly materials. These materials are designed to reduce environmental impact while maintaining high performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Busbars are a fundamental component of modern electrical systems, offering numerous advantages over traditional wiring methods. Their efficiency, reliability, and versatility make them indispensable in a wide range of applications, from power distribution systems to renewable energy installations. As technology continues to advance, busbars will play an increasingly important role in meeting the demands of contemporary electrical systems.
Whether you are designing a new electrical system or upgrading an existing one, understanding the various types of busbars and their applications is essential. By selecting the right busbar for your needs and ensuring proper installation and maintenance, you can enhance the performance and reliability of your electrical system.
In conclusion, busbars are not just a component; they are a critical element that ensures the smooth operation of electrical systems across various industries. By leveraging the benefits of busbars, you can achieve greater efficiency, reliability, and scalability in your electrical installations.


Comments are closed.